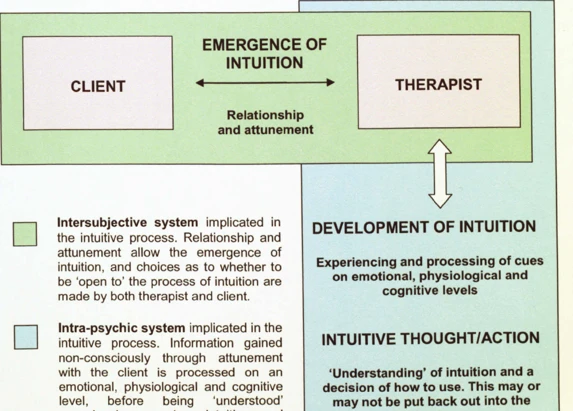
Have you ever had a gut feeling or a hunch that turned out to be right? That’s intuition at work. Understanding intuition is a fascinating topic that has intrigued psychologists and parapsychologists for years. In this article, we will delve into the world of intuition and explore insights from psychology and parapsychology. From defining intuition and exploring its historical perspective to unraveling the science behind it and discovering ways to develop and harness our own intuitive abilities, this article will provide you with a comprehensive understanding of intuition and how it influences our thoughts and actions. So, let’s embark on this journey of self-discovery and unravel the mysteries of intuition together!
Contents
- What is Intuition?
- Exploring Intuition through Psychology
- Parapsychology and Intuition
- Unraveling the Science Behind Intuition
- Developing and Harnessing Intuition
- Conclusion
-
Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. What are the different types of intuition?
- 2. Is intuition the same as instinct?
- 3. Can intuition be developed?
- 4. Is intuition always accurate?
- 5. Can intuition be learned and taught?
- 6. Can intuition be used in professional settings?
- 7. Can skepticism and intuition coexist?
- 8. Are women more intuitive than men?
- 9. Are there any risks in relying solely on intuition?
- 10. How can intuition be applied in everyday life?
- References
What is Intuition?

1. Defining Intuition: Intuition is a complex and elusive phenomenon that can be difficult to define precisely. It is often described as a form of knowing or understanding without the need for conscious reasoning or logical analysis. It is a sense of inner knowledge that arises spontaneously and effortlessly. Intuition can manifest as a gut feeling, a sudden insight, or a sense of certainty about a certain course of action. While it may seem mysterious, intuition has been studied and explored by psychologists and parapsychologists to better understand its nature and mechanisms.
2. Historical Perspective: The concept of intuition has been recognized and valued throughout history in various cultures. In ancient Greek philosophy, intuition was seen as a divine gift, a direct communication from the gods. In more recent times, philosophers and thinkers have offered different perspectives on intuition. René Descartes, a 17th-century philosopher, believed that intuition was a fundamental part of human understanding and knowledge. Sigmund Freud, the founder of psychoanalysis, viewed intuition as a product of the unconscious mind, influenced by repressed desires and instincts. These different perspectives highlight the diverse interpretations of intuition throughout history and its significance in human experience.
By understanding the definition and historical context of intuition, we can begin to explore the intricate mechanisms and potential applications of this intriguing phenomenon. Examining the fascinating field of psychology can shed light on the inner workings of intuition and how it influences our thoughts, decisions, and actions. So, let’s delve deeper into the fascinating world of intuition and discover the insights provided by psychology.
1. Defining Intuition
– Intuition is a complex and multifaceted concept that has been studied and defined in various ways. One common definition is that intuition is a form of knowledge or understanding that arises spontaneously and effortlessly, without conscious reasoning or logical analysis. It is often described as a gut feeling or a sense of inner knowing. Intuition can guide us in making decisions, solving problems, and navigating our daily lives. It operates on a subconscious level, drawing on information and experiences that may not be immediately accessible to our conscious awareness.
– According to psychologist Gary Klein, intuition is not a mystical or magical ability, but rather a result of expertise and pattern recognition. He suggests that intuition is developed through extensive experience in a particular domain, allowing individuals to recognize familiar patterns and make quick judgments based on those patterns.
– In the field of parapsychology, intuition is often associated with extrasensory perception (ESP) and psychic abilities. Some researchers argue that intuition goes beyond our conscious awareness and taps into a collective unconscious or a universal source of knowledge. However, the scientific study of parapsychology and psychic phenomena remains controversial and is not widely accepted by the mainstream scientific community.
– It is important to note that intuition is not infallible and can be influenced by cognitive biases and heuristics. These biases can lead to errors in judgment and decision-making. However, with awareness and practice, it is possible to strengthen and refine our intuitive abilities. Various techniques and exercises, such as meditation, mindfulness, and visualization, can help enhance intuition and enable individuals to tap into their inner wisdom.
To learn more about strengthening intuition, you can check out our article on 4 Exercises to Strengthen Your Intuition. By understanding the nature and definition of intuition, we can explore its fascinating role in human cognition and decision-making processes.
2. Historical Perspective
In exploring the historical perspective of intuition, we encounter fascinating insights from various philosophical and psychological perspectives. One prominent figure in the history of intuition is Carl Jung, a Swiss psychiatrist and founder of analytical psychology. Jung believed that intuition was one of four psychological functions, alongside sensation, thinking, and feeling. He saw intuition as a way of perceiving information beyond the realm of conscious awareness, accessing a collective unconscious that contains archetypes and universal symbols. Jung’s work emphasized the importance of intuition in psychological development and the exploration of the self.
Another influential thinker in the field of intuition is William James, an American philosopher and psychologist. James suggested that intuition arises from the subconscious mind and involves quick and immediate knowing. He argued that intuition could provide valuable insights and help guide decision-making without the need for extensive analysis. He believed that intuition was closely tied to individual experience and could be cultivated through personal growth and introspection.
Throughout history, intuition has been recognized as a valuable source of guidance, inspiration, and creativity. From ancient philosophical traditions to modern psychological theories, the historical perspective on intuition showcases its enduring significance. Understanding the historical context allows us to appreciate the rich tapestry of ideas and insights that have shaped our understanding of intuition. By incorporating these perspectives into our exploration, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the power of intuition in our lives. To further explore the science and development of intuition, you can check out this guide.
Exploring Intuition through Psychology

1. Dual-Process Theory: One prominent approach to understanding intuition is through the lens of dual-process theory. This theory suggests that our thinking and decision-making processes operate on two distinct systems: the intuitive system and the analytical system. The intuitive system, also known as System 1, is fast, automatic, and operates largely on unconscious processes. It is responsible for our intuitive judgments and quick assessments of situations. On the other hand, the analytical system, also known as System 2, is slower, deliberate, and relies on conscious reasoning and logical analysis. According to dual-process theory, intuition plays a vital role in guiding our initial impressions and snap judgments, while analytical thinking steps in to evaluate and override those intuitions when necessary.
2. The Power of the Unconscious Mind: Intuition is closely linked to the power of the unconscious mind. Our unconscious mind processes vast amounts of information and taps into past experiences and knowledge that may not be readily accessible to our conscious awareness. Research has shown that our unconscious mind can make accurate assessments and predictions, often shaping our intuitive responses. This suggests that our intuition can draw upon information that is beyond our conscious comprehension, guiding us towards insights and solutions that we may not be able to explain rationally. This aspect of intuition highlights the intricate interplay between our conscious and unconscious cognitive processes.
3. Emotional Cognition: Emotions play a significant role in intuition and decision-making. Studies have shown that our emotional state can influence the accuracy of our intuitive judgments. Positive emotions, such as joy or excitement, can enhance our intuitive abilities and lead to more accurate judgments. Conversely, negative emotions, such as fear or anxiety, can cloud our intuition and lead to biased or inaccurate judgments. This suggests that being aware of and managing our emotions can have a profound impact on the quality of our intuitive decision-making. By understanding the role of emotions in intuition, we can learn to leverage our emotional state to enhance our intuitive abilities.
By exploring these psychological insights into intuition, we gain a deeper understanding of how our mind processes information, makes judgments, and arrives at intuitive insights. Understanding the interplay between our intuitive and analytical processes can provide us with valuable tools for harnessing and trusting our intuition in various aspects of life. To learn effective tips and techniques for trusting and strengthening your intuition, check out this article on how to trust your intuition.
1. Dual-Process Theory
Dual-process theory is a psychological framework that helps us understand the role of intuition in decision-making. According to this theory, there are two distinct cognitive processes at play: the intuitive system and the analytical system. The intuitive system is fast, automatic, and operates largely on unconscious processes. It relies on heuristics, or mental shortcuts, to quickly assess situations and make judgments. On the other hand, the analytical system is slow, deliberate, and conscious. It involves logical reasoning, careful evaluation of evidence, and systematic analysis of information. The interaction between these two systems determines our decision-making process.
Research has shown that intuition often plays a crucial role in decision-making. Sometimes, relying on our gut feelings can lead to better decisions than purely analytical thinking. This is particularly true in situations where there is a wealth of information to consider or when time is limited. However, intuition is not infallible, and it can be influenced by biases and heuristics. This is why a balanced approach that integrates both intuition and analytical thinking is often recommended.
Understanding the dual-process theory can help us appreciate the power of intuition and how it complements our rational thinking. By recognizing the value of intuitive insights, we can learn to trust our gut feelings in certain situations. Additionally, being aware of the potential biases and limitations of intuition can help us make more informed decisions. So, let’s delve deeper into the fascinating interplay between intuition and rational thinking as we explore the power of the unconscious mind.
2. The Power of the Unconscious Mind
Our unconscious mind plays a significant role in our intuitive processes. It is a vast reservoir of information and experiences that may not be readily accessible to our conscious awareness. The unconscious mind processes information effortlessly and can detect subtle patterns and connections that we may not consciously perceive. This allows it to contribute to our intuitive insights.
Research has shown that the unconscious mind is adept at recognizing complex patterns and making connections between seemingly unrelated pieces of information. This ability is often referred to as “implicit learning.” When we are faced with a decision or problem, our unconscious mind works behind the scenes, analyzing and integrating various factors and information to provide us with intuitive insights.
The power of the unconscious mind in intuition is evident in various situations. For example, have you ever had a “gut feeling” about a person or situation that you couldn’t logically explain? This may be your unconscious mind picking up on subtle cues and nonverbal communication that your conscious mind may have missed. Additionally, our unconscious mind can also draw upon past experiences and memories, enabling us to make quick judgments or decisions based on prior knowledge, even if we can’t consciously remember the specifics.
It’s important to note that while our unconscious mind can provide valuable insights, it is not infallible. Sometimes, our unconscious biases or assumptions can influence our intuitive judgments. To harness the power of the unconscious mind effectively, we need to cultivate self-awareness and critical thinking skills. By being mindful of our biases and actively engaging in reflective thinking, we can enhance the accuracy and reliability of our intuitive insights.
Understanding the role of the unconscious mind in intuition is crucial in appreciating and utilizing this innate capacity. As we explore further, we will delve into the fascinating field of emotional cognition and how our emotions can also influence and enhance our intuitive processes.
3. Emotional Cognition
3. Emotional Cognition: Emotional cognition refers to the idea that emotions play a crucial role in our intuitive processes. Our emotions can provide valuable information and signals that guide our decision-making and intuition. Research has shown that our emotional states can influence our intuitive judgments and perceptions. For example, studies have found that individuals in a positive emotional state are more likely to make intuitive decisions based on “gut feelings,” while those in a negative emotional state tend to rely more on deliberate analysis and logic.
One theory that explains the connection between emotions and intuition is the somatic marker hypothesis proposed by Antonio Damasio. According to this hypothesis, our emotional responses are linked to bodily sensations that arise in response to different situations and experiences. These bodily sensations serve as markers that guide our decision-making by signaling the emotional significance of a particular choice or action. In other words, our emotions provide us with intuitive signals that help us make quick and adaptive decisions.
Research has demonstrated that certain emotions can enhance certain aspects of intuition. For instance, positive emotions such as joy and gratitude have been found to enhance creativity and the generation of novel ideas. On the other hand, negative emotions like fear and sadness can narrow our focus and heighten our attention to details, leading to more cautious and precise intuitive judgments.
Understanding the role of emotions in intuition can help us become more aware of how our emotional states influence our decision-making processes. By recognizing and harnessing the power of emotional cognition, we can tap into our intuition and make more informed and balanced decisions in various aspects of our lives.
References:
– Damasio, A. (1994). Descartes’ Error: Emotion, Reason, and the Human Brain. New York: Putnam.
– Tamir, M., Chiu, C., & Gross, J. J. (2007). Business or pleasure? Utilitarian versus hedonic considerations in emotion regulation. Emotion, 7(3), 546-554. doi: 10.1037/1528-3542.7.3.546
Parapsychology and Intuition

1. Research on Extrasensory Perception (ESP): Parapsychology, a field of study that investigates phenomena beyond the scope of traditional scientific explanations, has long been interested in the connection between intuition and abilities such as extrasensory perception (ESP). ESP refers to the ability to acquire information through means other than the known senses. Research in parapsychology has examined various forms of ESP, including telepathy, clairvoyance, and precognition. While controversial and often met with skepticism, studies have shown intriguing results suggesting that some individuals may possess intuitive abilities that transcend conventional understanding.
2. Telepathy and Intuition: Telepathy, the ability to communicate thoughts or information without any apparent physical connection, is closely related to intuition. Parapsychological research has explored the phenomenon of telepathy in laboratory settings, using methods such as sender-receiver experiments. These experiments involve one person attempting to transmit information to another person without the use of any known sensory channels. While the results of telepathy research have been mixed and the exact mechanisms remain unclear, they provide tantalizing evidence for the existence of non-verbal communication and intuitive connections between individuals.
3. Premonitions and Precognition: Parapsychology has also investigated the phenomenon of premonitions and precognition, which involve a sense of knowing or predicting future events before they occur. Some individuals claim to have experienced premonitions or precognitive dreams, providing insight into potential future outcomes. Parapsychological studies have attempted to understand these experiences by conducting experiments that examine the validity and accuracy of such predictions. While the scientific consensus on the existence and reliability of premonitions is still debated, research in parapsychology continues to explore the boundaries of human intuition and its potential in perceiving future events.
Through the lens of parapsychology, we gain a unique perspective on intuition and its connection to phenomena that challenge traditional scientific explanations. While the findings in parapsychology are not universally accepted, they provoke thought and spark curiosity about the nature of intuitive abilities. By examining the research conducted in this field, we can expand our understanding of intuition and consider new possibilities beyond the confines of conventional scientific knowledge.
1. Research on Extrasensory Perception (ESP)
1. Research on Extrasensory Perception (ESP): Extrasensory perception, commonly referred to as ESP, is a phenomenon that falls within the realm of parapsychology. It encompasses various abilities that go beyond the five traditional senses of sight, hearing, taste, smell, and touch. Research in parapsychology seeks to explore and understand these seemingly supernatural abilities.
One area of research within ESP focuses on telepathy, which refers to the ability to communicate thoughts or feelings from one person’s mind to another’s without the use of traditional forms of communication. Studies have been conducted to investigate whether individuals can accurately perceive and transmit information from one mind to another through telepathic means. Some experiments have shown statistically significant results, suggesting that telepathic communication may indeed exist.
Another facet of ESP research explores the phenomena of precognition and premonitions. Precognition refers to the ability to perceive or predict future events that cannot be inferred through logical reasoning or sensory information. Premonitions, on the other hand, involve intuitive feelings or forewarnings about future events. While the scientific community remains divided on the validity of these phenomena, various studies have been conducted to examine the existence and accuracy of precognition and premonitions.
It is important to note that ESP research has faced significant controversy and skepticism in the scientific community. Critics argue that the findings are often inconclusive, and the methodologies used lack scientific rigor. However, proponents of parapsychology continue to pursue research endeavors to expand our understanding of these extraordinary abilities.
By exploring the research on ESP, we can gain insights into the potential existence of abilities that go beyond our conventional senses. The findings from this branch of parapsychology contribute to the broader understanding of intuition and its connection to unexplained phenomena.
2. Telepathy and Intuition
2. Telepathy and Intuition: Telepathy is often closely associated with intuition, as both involve the transmission and reception of information beyond traditional sensory channels. Telepathy refers to the ability to communicate thoughts, ideas, or emotions between individuals without the use of conventional means of communication. While telepathy is often considered a more paranormal phenomenon, it is worth exploring its connection to intuition.
Some researchers propose that telepathy may be an extension of intuitive abilities, allowing individuals to tap into a shared collective consciousness or a universal information field. It is believed that intuitive individuals may be more receptive to telepathic communication, as their heightened sensitivity allows them to pick up on subtle signals or energies that others may miss.
However, it’s important to note that the scientific evidence for telepathy remains controversial and inconclusive. While some studies have shown intriguing results, they have not been able to definitively prove the existence of telepathic abilities. Nevertheless, the exploration of telepathy in relation to intuition offers a fascinating avenue for further investigation and understanding of the complexities of human consciousness and perception.
To learn more about developing and honing your intuition, check out our article on science-backed techniques and exercises to strengthen your intuitive abilities.
3. Premonitions and Precognition
3. Premonitions and Precognition: Premonitions and precognition are phenomena within parapsychology that relate to the ability to perceive or predict future events. Premonitions are intuitive feelings or sensations that warn of an upcoming event or situation, often associated with a sense of foreboding or unease. These experiences can range from vague feelings to vivid and detailed visions. Precognition, on the other hand, refers to the ability to foresee or know about future events before they happen, often without any apparent logical or sensory explanation. These experiences can occur through dreams, flashes of insight, or strong intuitive impressions.
The existence of premonitions and precognition has been a subject of both fascination and skepticism. While some individuals report experiencing these phenomena, they are often met with skepticism and disbelief due to the lack of scientific evidence. However, numerous studies and anecdotal accounts have provided intriguing glimpses into the potential reality of these phenomena.
One notable aspect of premonitions and precognition is that they often appear to be more prevalent in times of crisis or significant personal or collective events. For example, there are historical accounts of individuals having premonitions before natural disasters, accidents, or major societal shifts. While the exact mechanisms behind these experiences remain unknown, they raise questions about the nature of time and the limits of human perception.
Psychologists and parapsychologists continue to study premonitions and precognition in an attempt to understand their origins and mechanisms. Research in parapsychology aims to explore the potential existence of psychic phenomena, including the ability to predict future events. Understanding these phenomena can provide valuable insights into the nature of consciousness, time, and the potential capabilities of the human mind.
While premonitions and precognition may seem mysterious and elusive, they contribute to the broader understanding of intuition and its potential beyond conventional conscious awareness. Exploring these phenomena allows us to expand our perspectives on the nature of reality and the untapped potentials of the human mind.
Unraveling the Science Behind Intuition

1. Neurological Basis of Intuition: Scientists have been studying the neurological basis of intuition to unravel the science behind this phenomenon. Neuroimaging studies have shown that intuition involves the rapid processing of information in various regions of the brain, including the prefrontal cortex, the anterior cingulate cortex, and the insula. These brain areas are associated with emotions, decision-making, and the integration of information from different sources. Additionally, research suggests that intuition is closely linked to the body’s physiological responses, such as heart rate and skin conductance, indicating the involvement of the autonomic nervous system in these intuitive processes.
2. Cognitive Biases and Heuristics: Another aspect of the science behind intuition lies in the influence of cognitive biases and heuristics on our intuitive judgments. Cognitive biases are systematic errors in thinking that can influence our decision-making processes. For example, the availability heuristic leads us to rely on readily available information when making judgments, even if it’s not the most accurate or representative. These biases can sometimes lead to intuitive insights that align with reality, but they can also result in errors and faulty judgments. Understanding these biases and heuristics can help us become more aware of our intuitive processes and improve our decision-making.
3. Intuition as Pattern Recognition: One theory proposed by psychologists is that intuition is a result of pattern recognition. Our brains are constantly processing vast amounts of information and looking for familiar patterns. Intuition occurs when these patterns are recognized unconsciously, leading to a “feeling” or “knowing” without explicit reasoning. This pattern recognition process allows us to make quick, intuitive judgments based on our past experiences and expertise. Research has shown that experts in various domains, such as chess players or doctors, rely heavily on intuition derived from their extensive experience and pattern recognition abilities.
By unraveling the science behind intuition, we gain a deeper understanding of the underlying processes that drive our intuitive insights. The neurological basis, cognitive biases, and pattern recognition all contribute to our intuitive abilities. Recognizing these factors can help us harness and develop our intuition to make more informed and effective decisions in various aspects of our lives. To learn more about the science of developing intuition, you can check out this informative article on science-developing-intuition.
1. Neurological Basis of Intuition
The field of neuroscience has made significant progress in uncovering the neurological basis of intuition. Studies have shown that intuition is closely linked to the brain’s ability to process information and make quick judgments based on past experiences and patterns.
1. Intuitive Processing: Neuroimaging studies have revealed that intuitive processing involves the activation of brain regions such as the anterior cingulate cortex and the insula. These areas are associated with emotional processing and decision-making. It suggests that intuition may be influenced by emotional cues and subjective experiences.
2. Pattern Recognition: The brain is a pattern-seeking organ, constantly searching for familiar patterns and associations. Intuition relies on the brain’s ability to recognize and match patterns quickly and unconsciously. This process occurs in brain regions such as the hippocampus and the prefrontal cortex, which are involved in memory and executive functions.
3. Intuitive Insights: Research has also shown that intuitive insights often arise from the brain’s default mode network (DMN). This network is active during rest or when the mind is wandering. It suggests that intuition may emerge when the brain is in a relaxed state, allowing for creative and unconventional connections to be made.
Understanding the neurological basis of intuition provides valuable insights into how our brain processes information and makes intuitive judgments. It highlights the intricate interplay between cognitive processes, emotions, and past experiences. By unraveling the science behind intuition, we can gain a deeper appreciation for this fascinating aspect of human cognition and decision-making.
2. Cognitive Biases and Heuristics
2. Cognitive Biases and Heuristics: When it comes to understanding intuition, cognitive biases and heuristics play a significant role. Cognitive biases are mental shortcuts or patterns of thinking that can lead to systematic deviations from logic and rationality. These biases can influence our decision-making and perception without us even realizing it. For example, confirmation bias is the tendency to seek out information that confirms our preexisting beliefs or opinions while ignoring contradictory evidence. This bias can strongly impact how we interpret intuitive feelings or insights.
On the other hand, heuristics are mental strategies or shortcuts that allow us to make quick judgments or decisions based on limited information. They can be seen as rules-of-thumb that our brains use to simplify complex problems and reduce cognitive load. While heuristics can be helpful in certain situations, they can also contribute to biases in our intuitive thinking. For instance, the availability heuristic leads us to rely on immediate examples that come to mind when making judgments, even if those examples may not accurately represent the overall probability.
Understanding these cognitive biases and heuristics is vital as they can both enhance and hinder the accuracy of our intuitive judgments. By being aware of these biases, we can consciously challenge and evaluate our intuitive responses, allowing for more reliable and informed decision-making. Developing critical thinking skills and actively questioning our assumptions can help us mitigate the potential negative effects of cognitive biases and heuristics on our intuition.
In the next section, we will explore the fascinating process of the neurological basis of intuition and gain insights into how our brain functions in relation to intuitive experiences. Understanding the biological underpinnings of intuition can provide us with a deeper understanding of this phenomenon and its significance in human cognition and behavior. So, let’s dive into the realm of neuroscience and unravel the mysteries of intuition together.
Developing and Harnessing Intuition
1. Cultivating Self-Awareness: Developing intuition starts with cultivating self-awareness. This involves paying attention to our thoughts, emotions, and physical sensations. By being mindful of our inner experiences, we can become more attuned to the subtle signals and cues that intuition often communicates through. Practices such as meditation, journaling, and self-reflection can help enhance self-awareness and create a stronger connection with our intuitive abilities.
2. Mindfulness and Intuition: Mindfulness, the practice of being fully present in the moment, can also play a significant role in developing and harnessing intuition. When we are mindful, we are more open and receptive to the information that our intuition provides. By quieting the chatter of the mind and being fully engaged in the present, we can tap into our intuitive insights more easily. Incorporating mindfulness techniques into our daily lives, such as mindful breathing or body scans, can enhance our ability to access and trust our intuition.
3. Intuitive Decision-Making: Intuition can be a valuable tool for making decisions, especially when faced with complex or ambiguous situations. Intuitive decision-making involves combining rational analysis with our gut instincts. It is important to give ourselves permission to trust our intuition and integrate it into our decision-making process. This can be achieved by evaluating the pros and cons, gathering relevant information, and then tuning in to our intuitive responses. It’s essential to weigh the logical aspects of a situation with our intuitive insights, as this holistic approach can lead to more informed and satisfying decisions.
By intentionally cultivating self-awareness, incorporating mindfulness practices, and embracing intuitive decision-making, we can develop and harness our intuition in a meaningful way. Trusting our intuition can bring a sense of clarity and guidance to our lives, enabling us to make choices that align with our deepest values and aspirations. So, let’s continue our journey of self-discovery and explore the vast potential of intuition in our personal and professional lives.
1. Cultivating Self-Awareness
1. Cultivating Self-Awareness: Self-awareness is a crucial component when it comes to harnessing intuition. To cultivate self-awareness, it’s important to develop a deep understanding of oneself, including our thoughts, emotions, and patterns of behavior. Here are some strategies to enhance self-awareness and strengthen intuition:
a) Mindfulness Practice: Engaging in mindfulness practices such as meditation can help increase self-awareness. By intentionally focusing one’s attention on the present moment without judgment, individuals can develop a greater understanding of their thoughts, emotions, and bodily sensations. This heightened awareness can enhance the ability to recognize intuitive signals.
b) Journaling: Keeping a journal can be a valuable tool for self-reflection. By regularly writing down thoughts, feelings, and experiences, individuals can gain insight into their inner world. Journaling can help identify patterns, triggers, and recurring themes that may influence intuitive guidance.
c) Seeking Feedback: Actively seeking feedback from others can provide valuable perspectives and insights into one’s strengths, weaknesses, and blind spots. Trusted individuals, such as mentors or close friends, can offer objective observations and help identify areas for personal growth and self-awareness.
d) Emotional Awareness: Developing emotional awareness involves recognizing and understanding one’s own emotions and how they impact decision-making processes. Emotions serve as valuable indicators and can provide important intuitive signals. By learning to tune into and interpret emotional states, individuals can better access their intuition.
By cultivating self-awareness through mindfulness practice, journaling, seeking feedback, and developing emotional awareness, individuals can enhance their ability to tap into and trust their intuition. Self-awareness serves as a foundation for harnessing intuition and making more informed decisions in various aspects of life. To further explore methods of developing intuition, check out these exercises designed to strengthen intuitive abilities.
2. Mindfulness and Intuition
2. Mindfulness and Intuition: Mindfulness, often associated with meditation practices, is a state of present-moment awareness and non-judgmental acceptance. It involves intentionally focusing one’s attention on the present experience, including thoughts, feelings, and bodily sensations. This heightened state of awareness can have a profound impact on intuition.
When we practice mindfulness, we develop the ability to observe our thoughts and emotions without attachment or judgment. This allows us to tap into our intuitive insights more readily. By becoming aware of the present moment, we can quiet the noise of our busy minds and create space for intuitive thoughts and feelings to arise.
Research has shown that mindfulness can enhance our intuitive abilities in several ways. Firstly, it improves our self-awareness, enabling us to recognize and trust our intuitive signals. Mindfulness helps us become attuned to subtle bodily sensations and emotions, which are often indicators of our intuition speaking to us.
Secondly, mindfulness helps us cultivate a sense of curiosity and open-mindedness. By adopting a non-judgmental attitude toward our thoughts and experiences, we become more receptive to new ideas and insights. This openness allows us to tap into our intuition and consider alternative perspectives.
Lastly, mindfulness reduces the influence of cognitive biases and preconceived notions. When we are mindful, we can observe our thoughts and beliefs without automatically accepting them as absolute truths. This allows us to bypass cognitive biases and approach situations with a fresh and intuitive mindset.
Practicing mindfulness can be a powerful tool for developing and harnessing our intuitive abilities. By integrating mindfulness into our daily lives, we can cultivate a deeper connection with our intuition and make more informed decisions. If you’re interested in incorporating mindfulness practices to enhance your intuition, check out these helpful resources: [link text](/science-developing-intuition/).
3. Intuitive Decision-Making
Making decisions is a fundamental aspect of our daily lives, and intuition plays a significant role in this process. Intuitive decision-making involves relying on our instinctive feelings and immediate insights to guide our choices, rather than solely relying on conscious reasoning and analysis. Here are some key points to understand about intuitive decision-making:
1. Fast and Automatic: Intuitive decision-making is characterized by its speed and automaticity. It occurs rapidly and effortlessly, often bypassing conscious deliberation. This process allows us to make quick decisions in situations where time is limited or complex information overload may hinder rational analysis.
2. Pattern Recognition: Intuition harnesses our ability to recognize patterns and make connections based on past experiences and accumulated knowledge. Through pattern recognition, our brain processes and synthesizes vast amounts of information quickly, leading to intuitive insights and judgments.
3. Emotional Signals: Emotions play a vital role in intuitive decision-making. Our bodies and brains send signals in the form of feelings and bodily sensations that can provide valuable guidance. These emotional signals can help us evaluate the potential outcomes of a decision and guide us toward choices that align with our values and desires.
4. Expertise and Experience: Intuition is closely linked to expertise and experience. As individuals gain expertise in a specific field or domain, their intuitive decision-making abilities improve. Experts often rely heavily on intuition to make complex judgments and solve problems quickly, drawing from their extensive knowledge and past experiences.
5. Trust and Confidence: Intuition requires trust and confidence in oneself. It involves having faith in our subconscious and its ability to process information and guide us toward the right decision. Trusting our intuition can help reduce self-doubt and enhance our overall decision-making abilities.
6. Limitations: While intuitive decision-making can be powerful, it is not without its limitations. Intuition can be influenced by cognitive biases, personal beliefs, and cultural factors. It may also lead to errors in judgment when faced with novel or unfamiliar situations that don’t align with past experiences.
7. Enhancing Intuitive Decision-Making: There are several strategies to enhance intuitive decision-making, such as cultivating self-awareness, practicing mindfulness, and seeking diverse perspectives. These techniques can help us develop a deeper understanding of our own intuitive processes and make more informed decisions.
Incorporating intuition into our decision-making processes can lead to more holistic and insightful choices. By recognizing the role of intuition and understanding how to harness its power, we can navigate through complex decisions with greater clarity and confidence. In the next section, we will explore practical ways to develop and harness our intuition effectively.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the study of intuition from the combined perspectives of psychology and parapsychology offers valuable insights into this intriguing phenomenon. Through the exploration of dual-process theory, the power of the unconscious mind, emotional cognition, and neurobiology, we begin to unravel the science behind intuition. Additionally, parapsychological research into extrasensory perception, telepathy, and premonitions adds another layer of understanding to the complexities of intuitive experiences. Developing and harnessing intuition is a personal journey that involves cultivating self-awareness, practicing mindfulness, and honing intuitive decision-making skills. By understanding and embracing our intuitive abilities, we can tap into a valuable source of knowledge and guidance. Trusting our intuition can lead to more informed decisions, enhanced creativity, and a deeper connection with ourselves and the world around us. So, let us continue to explore and nurture our intuition, harnessing its power to enrich our lives.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are the different types of intuition?
Intuition can be categorized into different types based on how it manifests. These types include cognitive intuition, where insights and solutions arise from unconscious mental processes; emotional intuition, which involves using feelings and emotions to guide decision-making; and spiritual intuition, which is a deep sense of connection to something greater than oneself.
2. Is intuition the same as instinct?
No, intuition and instinct are different. Instincts are innate, primal behaviors that are hardwired in us, while intuition is a form of higher-level knowing that goes beyond instinctual responses. Intuition involves a sense of understanding or insight that is not necessarily based on physical or survival-related factors.
3. Can intuition be developed?
Yes, intuition can be developed and strengthened through practices such as mindfulness, meditation, and self-reflection. Cultivating self-awareness and learning to trust one’s inner guidance can enhance intuitive abilities.
4. Is intuition always accurate?
Intuition is not always accurate, as it can be influenced by biases, emotions, and personal beliefs. It is important to approach intuition with a healthy dose of critical thinking and consider other sources of information before making important decisions based solely on intuition.
5. Can intuition be learned and taught?
While some individuals may have a natural inclination towards intuitive thinking, everyone has the potential to develop their intuitive abilities. Techniques such as journaling, participating in intuition exercises, and seeking feedback from others can help in learning and honing intuitive skills.
6. Can intuition be used in professional settings?
Absolutely! Intuition can be a valuable tool in professional settings such as business, leadership, and creative industries. It can help in problem-solving, decision-making, and generating innovative ideas. Many successful professionals rely on their intuition as a guide in their decision-making process.
7. Can skepticism and intuition coexist?
Yes, skepticism and intuition can coexist. While skepticism encourages critical thinking and questioning, intuition can provide valuable insights and alternative viewpoints. Both skepticism and intuition have their place in decision-making and can complement each other when used in a balanced manner.
8. Are women more intuitive than men?
There is no scientific evidence to support the notion that women are inherently more intuitive than men. Intuitive abilities are not gender-specific and can vary among individuals, irrespective of their gender.
9. Are there any risks in relying solely on intuition?
Relying solely on intuition can have risks, especially in situations where logical analysis and evidence-based decision-making are crucial. It is important to strike a balance between intuition and reasoning to make well-informed and effective choices.
10. How can intuition be applied in everyday life?
Intuition can be applied in everyday life by paying attention to gut feelings, listening to inner guidance, and using intuition as a tool for self-discovery and problem-solving. Trusting and following your intuition can lead to better decision-making and a deeper understanding of oneself.